The World Health Organization (WHO) provides significant insights into the status of tobacco consumption in India and its impact on oral cancer. Here’s a summary based on WHO’s observations and reports:
- Prevalence: India has one of the highest rates of tobacco consumption in the world. According to WHO and various national surveys, a substantial portion of the Indian population uses tobacco in some form—whether as cigarettes, beedis (a type of Indian cigarette), or smokeless tobacco products.
- Demographics: Tobacco use is widespread across various age groups and socioeconomic strata. However, it is particularly prevalent among males and tends to be higher in rural areas compared to urban settings. Smokeless tobacco products, such as gutkha, khaini, and paan, are also widely consumed.
- Health Risks: Tobacco use is a leading cause of several chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, respiratory disorders, and various cancers. India faces a significant burden from tobacco-related illnesses, which contribute heavily to the country’s overall disease burden and mortality rates.
Tobacco as a Threat to Oral Cancer
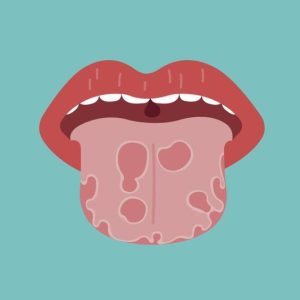
- Strong Association: Tobacco consumption is strongly linked to oral cancer. According to WHO, tobacco is one of the most significant risk factors for oral cancers, including cancers of the mouth, throat, and lips. The carcinogenic properties of tobacco, including both smoking and smokeless forms, are well-documented.
- High Incidence: India has one of the highest rates of oral cancer globally, largely attributable to tobacco use. Smokeless tobacco products are particularly associated with a higher incidence of oral cancer in India. The combination of tobacco with betel quid (paan) further increases the risk.
- Prevention and Control: WHO emphasizes the importance of tobacco control measures in reducing the incidence of oral cancer. This includes implementing strong anti-tobacco policies, such as higher taxes on tobacco products, public smoking bans, plain packaging, and comprehensive tobacco cessation programs. Educational campaigns to raise awareness about the dangers of tobacco use and promoting cessation support are also crucial.
- Surveillance and Research: WHO supports ongoing research and surveillance to better understand the patterns of tobacco use and its impact on health. This helps in designing targeted interventions and policies to address the tobacco-related cancer burden effectively.
In summary, WHO views tobacco consumption in India as a major public health issue, particularly in relation to oral cancer. Effective tobacco control strategies are essential to mitigate this threat and reduce the incidence of tobacco-related cancers in the country.
Sources:
For detailed and up-to-date information on tobacco consumption and its impact on health, including oral cancer, you can refer to the following sources from the World Health Organization (WHO) and other reputable organizations:
- WHO Global Report on Tobacco: This report provides comprehensive data on tobacco consumption, its impact on health, and global tobacco control efforts.
- WHO Tobacco Control: This page offers resources and information on tobacco control measures, including country-specific data and statistics.
- Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS) India: This survey provides detailed statistics on tobacco use and its health effects in India.
- GATS India
- National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP) India Reports: Reports on cancer statistics, including oral cancer incidence, in India.
- National Cancer Registry Programme Reports