Gynecologic Cancers Unveiled: Can PCOS Cause Ovarian Cancer and more through the Lens of an Ovarian Cancer Specialist
Gynecologic cancer refers to any cancer that begins in a woman’s reproductive organs, making all women potentially at risk. The five main types are cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar, with fallopian tube cancer being rare.
Types of Gynaecological Cancers We Treat:
Cervical cancer : Begins in the cervix (lower, narrow end of the uterus or womb).
Ovarian cancer : Begins in the ovaries (located on each side of uterus).
Uterine cancer : Begins in the uterus (pear-shaped organ in pelvis where baby grows).
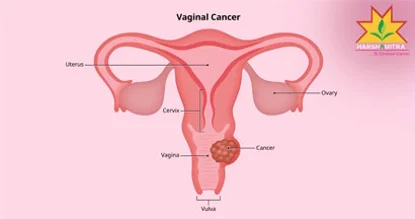
Vaginal cancer : Begins in the vagina (tube-like between uterus bottom and outside of body).
Vulvar cancer : Begins in the vulva (outer part of the female genital organs).
Causes and Risk factors
Each gynecologic cancer has unique risk factors and prevention strategies. A strong family history is the most significant risk factor for ovarian cancer, with one in five cases linked to inherited gene mutations. Obesity is associated with a rising incidence of endometrial cancer, while age is a major factor, as the risk for most gynecologic cancers increases after 60. Additionally, HPV, a sexually transmitted virus, is a key cause of cervical cancer and is also linked to vaginal and vulvar cancers.
Can PCOS Cause Ovarian Cancer?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. A study published in International Journal of Cancer in 2023 reported more than two times increased risk of ovarian cancer among postmenopausal women with PCOS and an increased risk of serious borderline ovarian tumours compared with women without PCOS.
Although the risk significantly high among postmenopausal women with PCOS, it is important for all women with PCOS to stay vigilant and consult an ovarian cancer specialist for routine screenings and health assessments.
Treatment options
Gynecologic cancers are treated using various methods depending on the type and stage of cancer, and most patients receive more than one form of treatment. Surgery involves removing the cancer through an operation. Chemotherapy uses special medicines, administered either as pills or through veins, to shrink or kill the cancer. Radiation therapy employs high-energy rays, similar to X-rays, to destroy cancer cells.
Symptoms
Recognizing the warning signs of gynecologic cancers is important, as symptoms vary for each type. Common symptoms include:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge (all except vulvar cancer).
Ovarian cancer: Bloating, feeling full quickly, difficulty eating, abdominal or back pain.
Ovarian and uterine cancers: Pelvic pain or pressure.
Ovarian and vaginal cancers: Frequent or urgent urination, constipation.
Vulvar cancer: Itching, burning, pain, tenderness, or changes in vulva color/skin, such as rashes, sores, or warts.
If you're still wondering, “Can PCOS cause ovarian cancer?”, the answer highlights the importance of monitoring your health. Women experiencing any of the above symptoms should seek guidance from an ovarian cancer specialist to address potential concerns promptly.
Book an Appointment
Seeking an expert consultation, Cancer Screenings, Conservative Surgeries, a second opinion, or immediate treatment, our state-of-the-art facility is ready to support you at every stage of your cancer journey. We prioritize your health and comfort, making the appointment process quick and easy. Take the first step towards specialized cancer care today.
What you can expect from us:
Expert Cancer Care : Specialized in all forms of cancer treatment, including curative, preventive, and palliative oncology
Advanced Technology : Featuring cutting-edge therapies like Linear Accelerator Radiation (LINAC) and 24-channel Brachytherap
Personalized Treatment Plans : Tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient, ensuring holistic care.
Preventing Gynecologic Cancer
Understanding your risk for gynecologic cancer and undergoing recommended testing, screening, and vaccinations are crucial for prevention. Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle is essential, as obesity is a significant risk factor for endometrial cancer. Women aiming for short- and long-term weight loss should prioritize healthy habits. Genetic testing is recommended for women with a family history of ovarian cancer, premenopausal breast cancer (before age 45), or a personal history of endometrial or colon cancer before age 50; consulting a genetic counselor is advisable in these cases. The HPV vaccine has proven highly effective in preventing cervical cancer, reducing HPV rates by 63% in teenage girls and 34% in women (20–24 years). It is recommended for men and women aged 11 to 26.
Testimonials
Frequently Asked Questions
PCOS does not directly cause ovarian cancer, but women with PCOS may have a slightly increased risk of developing endometrial cancer due to irregular periods. Regular screening is important for women with PCOS.
Common symptoms include abdominal bloating, pelvic pain, frequent urination, and difficulty eating. However, these symptoms can be vague, so regular checkups are crucial for early detection.
Ovarian cancer is typically treated with a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation. The treatment plan depends on the type and stage of the cancer.
Cervical cancer can often be detected early through regular Pap smears. Ovarian, endometrial, and other cancers may require advanced imaging and genetic tests for early detection.
Genetic counseling can help identify individuals with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations, which increase the risk of ovarian and breast cancers.
Women aged 21-65 should get a Pap smear every 3 years. After age 30, you can also opt for co-testing with an HPV test every 5 years if results are normal.
While PCOS does not directly cause ovarian cancer, it may increase the risk of endometrial cancer due to irregular periods. Regular screening is recommended for women with PCOS.
The CA-125 blood test measures the level of a protein that may be elevated in ovarian cancer. It’s used in conjunction with other tests like ultrasounds to detect ovarian cancer or monitor treatment effectiveness.
Yes, the HPV vaccine protects against the strains of HPV that most commonly cause cervical cancer. It is highly recommended for girls and boys from the age of 9 to 26.
If you have a family history, genetic testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be beneficial. Our genetic counselors can help assess your risk and guide preventive steps.