Cancer has emerged as a significant public health challenge in India, with the incidence and mortality rates rising steadily. The health sector, comprising government bodies, healthcare providers, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and private institutions, plays a crucial role in fostering cancer awareness among the public. This article delves into the multifaceted role of the health sector in enhancing cancer awareness and outlines the strategies employed to mitigate the impact of this disease on the Indian populace.
Current Cancer Scenario in India
India faces a daunting cancer burden, with an estimated 1.39 million new cases and 850,000 cancer-related deaths reported annually. 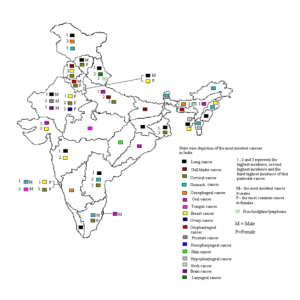 The most common cancers include breast, cervical, oral, and lung cancer. Early detection and timely intervention are vital to improving survival rates, making cancer awareness an essential component of public health initiatives.
The most common cancers include breast, cervical, oral, and lung cancer. Early detection and timely intervention are vital to improving survival rates, making cancer awareness an essential component of public health initiatives.
Government Initiatives
- National Cancer Control Programme (NCCP): The NCCP, initiated in 1975, aims to reduce cancer mortality by focusing on prevention, early detection, treatment, and palliative care. It has been instrumental in establishing Regional Cancer Centers (RCCs) and implementing public awareness campaigns.
- National Health Mission (NHM): Under the NHM, various programs such as the Ayushman Bharat scheme and the Health and Wellness Centers (HWCs) integrate cancer screening and awareness activities. These initiatives aim to provide accessible and affordable healthcare services, including cancer care, to the rural and underserved populations.
- Screening Programs: The government has launched population-based screening programs for common cancers like breast, cervical, and oral cancer. These programs focus on high-risk groups and promote early diagnosis through routine check-ups and awareness campaigns.
Role of Healthcare Providers
- Primary Care Providers: Primary care physicians and community health workers play a pivotal role in disseminating cancer-related information. They educate patients on risk factors, preventive measures, and the importance of regular screenings, thereby fostering a proactive approach to health.
- Specialized Cancer Centers: RCCs and other specialized cancer hospitals conduct awareness programs, workshops, and seminars to educate the public and healthcare professionals about the latest advancements in cancer detection and treatment. These centers also collaborate with schools, colleges, and workplaces to reach a broader audience.
- Telemedicine: The adoption of telemedicine has revolutionized cancer care, particularly in remote areas. Tele-consultations and tele-education platforms enable healthcare providers to spread awareness and provide expert advice, bridging the gap between urban and rural healthcare services.
Role of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
- Awareness Campaigns: NGOs like the Indian Cancer Society, Cancer Patients Aid Association, and CanSupport run extensive awareness campaigns targeting diverse populations. They utilize various media, including social media, radio, television, and print, to disseminate information on cancer prevention, symptoms, and the importance of early detection.
- Community Outreach Programs: NGOs conduct community outreach programs, health camps, and educational workshops to raise awareness at the grassroots level. These initiatives often focus on marginalized communities with limited access to healthcare facilities.
- Support Groups: Support groups and counseling services provided by NGOs offer emotional and psychological support to cancer patients and their families. They also educate caregivers on how to assist patients effectively.
Private Sector Contribution
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Many private companies engage in cancer awareness activities as part of their CSR initiatives. They organize health camps, sponsor awareness campaigns, and provide financial support for cancer research and treatment facilities.
- Health Insurance Providers: Insurance companies play a role in spreading awareness about cancer by offering specialized cancer insurance plans. They also conduct educational programs to inform policyholders about cancer risks and the benefits of regular screenings.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite significant efforts, several challenges hinder effective cancer awareness in India. These include:
- Limited Resources: Insufficient funding and resources in rural areas restrict the reach of awareness programs.
- Cultural Barriers: Stigma and misconceptions about cancer deter people from seeking timely medical help.
- Healthcare Access: Inadequate healthcare infrastructure and a shortage of trained medical professionals in remote areas impede early detection and treatment.
To overcome these challenges, a coordinated approach involving all stakeholders is essential. This includes:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships between government bodies, healthcare providers, NGOs, and the private sector to pool resources and expertise.
- Improved Infrastructure: Investing in healthcare infrastructure and training to ensure comprehensive cancer care services are available across the country.
- Public Education: Intensifying public education efforts to dispel myths and promote a culture of regular health check-ups.
Conclusion
The health sector in India plays a pivotal role in enhancing cancer awareness among the public. Through a combination of government initiatives, healthcare provider efforts, NGO activities, and private sector contributions, significant strides have been made in educating the populace about cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment. Continued collaboration and investment in this area are crucial to reducing the cancer burden and improving health outcomes for all Indians.

