Pancreatic cancer is a silent killer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making it one of the deadliest cancers. Let’s debunk myths, understand causes, and identify symptoms to raise awareness and promote early detection.
Myths:
- Myth: Pancreatic cancer only affects smokers.
Fact: While smoking increases the risk, many non-smokers develop pancreatic cancer.
- Myth: Pancreatic cancer is always fatal.
Fact: Early detection and treatment can improve survival rates.
Functions:
- Exocrine function: Produces digestive enzymes (e.g., amylase, lipase, trypsin) to break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in food.

- Endocrine function: Produces hormones like insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide to regulate blood sugar levels, metabolism, and digestive processes.
Significance:
- Blood sugar regulation: Insulin and glucagon help maintain normal blood sugar levels, preventing diabetes and related complications.
- Digestion and nutrient absorption: Pancreatic enzymes facilitate the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food.
- Metabolic regulation: Pancreatic hormones influence metabolic processes, such as energy production, storage, and utilization.
- Maintaining healthy gut function: Pancreatic secretions help regulate gut motility, secretion, and blood flow.
- Supporting overall health: The pancreas plays a role in immune function, inflammation regulation, and overall well-being.
Dysfunction or diseases affecting the pancreas, such as pancreatitis, diabetes, or pancreatic cancer, can have significant impacts on overall health, emphasizing the importance of this vital organ.
Causes:
Pancreatic cancer is often linked to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Smoking is the leading risk factor, accounting for 25% of cases. Other significant risk factors include obesity (15% of cases), diabetes (5-10% of cases), family history (5-10% of cases), and genetic mutations (BRCA2, p16, PALB2). Additionally, chronic pancreatitis, dietary factors (high red meat consumption), and occupational exposure to certain chemicals (pesticides, heavy metals) may contribute to the development of pancreatic cancer.
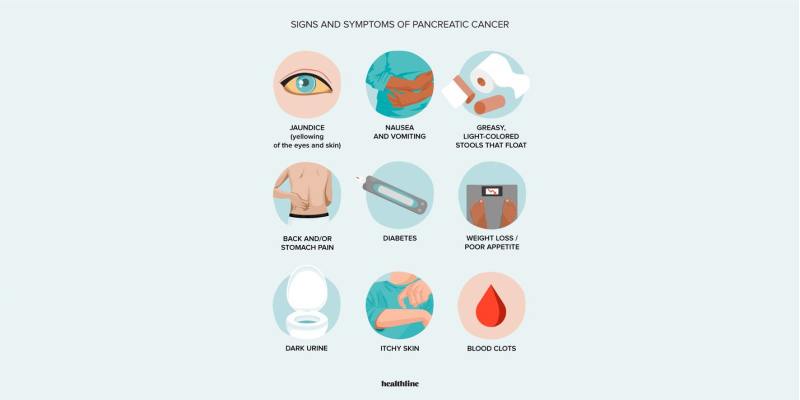
Symptoms:
Early-stage pancreatic cancer often presents with non-specific symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms include:
– Abdominal pain (30-40% of cases)
– Weight loss (20-30% of cases)
– Fatigue (15-20% of cases)
– Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes, 10-20% of cases)
– Dark urine and pale or greasy stools (5-10% of cases)
– Loss of appetite
– Nausea and vomiting
– Blood clots
– Recent-onset diabetes
As the disease progresses, symptoms worsen and may include:
– Severe abdominal pain
– Significant weight loss
– Ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen)
– Intestinal obstruction
Keep in mind that many of these symptoms can be attributed to other conditions, making early detection and diagnosis crucial for effective treatment.