Surgery has always been a cornerstone of modern medicine, providing crucial interventions that can save lives and significantly improve the quality of life for countless patients. With advancements in technology and medical practices, surgeries have evolved from invasive procedures to minimally invasive techniques, offering patients better outcomes and faster recovery times. Among the most notable advancements are radical, laparoscopic, and robotic surgeries. Each of these techniques has its unique benefits, applications, and outcomes, making them invaluable in the surgical landscape.
Radical Surgery: A Time-Tested Approach
Definition and Applications:
Radical surgery refers to an extensive procedure aimed at removing the entire diseased organ or tissue, often including surrounding lymph nodes or structures to ensure complete eradication of the disease, particularly cancer. This approach is commonly used in the treatment of cancers like breast cancer (radical mastectomy), prostate cancer (radical prostatectomy), and colorectal cancer.
Advantages:
– High Success Rate: Radical surgeries are highly effective in completely removing cancerous tissues, reducing the risk of recurrence.
– Comprehensive Treatment: By removing surrounding tissues and lymph nodes, radical surgery helps prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
Challenges:
– Invasiveness: The extensive nature of radical surgery often results in longer recovery times and higher chances of complications.
– Functional Impact: In some cases, radical surgery can lead to significant changes in bodily function, such as loss of organ function or changes in physical appearance.
Statistics:
– According to the American Cancer Society, radical prostatectomy has a 5-year survival rate of nearly 100% when cancer is detected early.
– Radical mastectomy, once the standard for breast cancer, has seen a significant decline in use, replaced by less invasive procedures, yet remains an option for certain aggressive cases.
Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally Invasive, Maximum Impact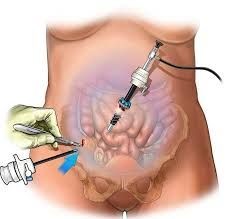
Definition and Applications:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS), involves small incisions through which a camera and surgical instruments are inserted to perform the operation. It’s commonly used for procedures like cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal), appendectomy, and hernia repair.
Advantages:
– Reduced Recovery Time: Due to smaller incisions, patients experience less pain and recover faster compared to traditional open surgery.
– Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions reduce the risk of postoperative infections.
– Minimal Scarring: The cosmetic results are often better, with smaller, less noticeable scars.
Challenges:
– Limited Scope: Not all surgeries can be performed laparoscopically, particularly those requiring extensive access to the affected area.
– Steep Learning Curve: Surgeons require specialized training and experience to perform laparoscopic surgeries effectively.
Statistics:
– The adoption of laparoscopic surgery has grown significantly, with a 40% reduction in recovery time and hospital stay compared to open surgery, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
– For colorectal surgeries, studies have shown that laparoscopic procedures result in similar cancer-related outcomes as open surgery but with fewer complications.
Robotic Surgery: The Future of Precision and Control
Definition and Applications:
Robotic surgery is an advanced form of laparoscopic surgery where surgeons use robotic systems, like the da Vinci Surgical System, to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision, flexibility, and control. It’s widely used in urological, gynecological, and cardiothoracic surgeries.
Advantages:
– Enhanced Precision: Robotic systems offer high-definition, 3D visualization and precision that surpasses human capabilities, allowing for more intricate and delicate procedures.
– Greater Control: Surgeons can perform complex movements with greater ease, reducing the risk of human error.
– Minimally Invasive: Like laparoscopic surgery, robotic surgery involves small incisions, leading to quicker recovery times and less postoperative pain.
Challenges:
– Cost: Robotic surgery is expensive, both in terms of equipment and procedure costs, making it less accessible in some regions.
– Operational Challenges: The complexity of robotic systems requires extensive training and experience, limiting the number of qualified surgeons.
Statistics:
– Robotic surgery has seen rapid adoption, particularly in prostate cancer treatment, with over 85% of prostatectomies in the U.S. now performed using robotic assistance.
– A study published in JAMA Surgery found that robotic surgery reduces the risk of surgical complications by 50% compared to open surgery in certain procedures.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Surgical Approach
The choice between radical, laparoscopic, and robotic surgery depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s expertise. Each approach offers distinct advantages and is suited to different situations. Radical surgery remains the gold standard for certain aggressive cancers, while laparoscopic surgery is preferred for less invasive needs, and robotic surgery offers unparalleled precision for complex cases.
As medical technology continues to advance, patients can expect even more refined techniques that enhance the efficacy of surgeries while minimizing risks and recovery times. Understanding the nuances of each surgical method empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions that lead to the best possible outcomes.

