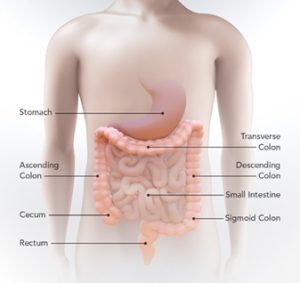
Colorectal cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the colon or rectum, collectively known as the colorectum. It typically begins as small, noncancerous polyps that can gradually transform into cancer over time. This type of cancer is prevalent worldwide, ranking among the leading causes of cancer-related deaths.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The certain risk factors include age, family history, and personal medical history play pivotal roles. Additionally, factors like a diet high in red and processed meats, low-fiber diets, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption contribute to an elevated risk.

Symptoms:
Symptoms of colorectal cancer can vary, but common signs include changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, abdominal discomfort, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment, making awareness of these signs vital.

Diagnosis and Screening:
Several diagnostic methods aid in detecting colorectal cancer. Colonoscopies, fecal occult blood tests, sigmoidoscopies, and imaging studies such as CT scans are utilized for accurate diagnosis. Regular screenings are recommended, especially for individuals with known risk factors or those above a certain age.

Screening Impact:
Regular screenings, such as colonoscopies and fecal occult blood tests, can contribute to the early detection of colorectal cancer, improving treatment outcomes.

tests for colorectal cancer.
It’s important to note that these statistics may have changed since my last update, and for the most current and specific information, it is recommended to consult reliable health organizations or databases. Additionally, advancements in research and healthcare may have influenced these figures since my last knowledge update.
Prevention:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco. Regular screenings, especially for individuals with risk factors, are essential for early detection and improved outcomes.
Incidence and Mortality:
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers globally.
It is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. In 2020, there were approximately 1.9 million new cases of colorectal cancer globally.
Risk Factors:
Family history, age, certain genetic conditions, a diet high in red and processed meats, lack of physical activity, and smoking are among the risk factors associated with colorectal cancer.
Conclusion:
Colorectal cancer is a serious health concern that demands attention and proactive measures. Understanding risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and participating in regular screenings are crucial components of prevention and early intervention. By prioritizing a healthy lifestyle and staying vigilant about potential signs, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate the impact of colorectal cancer.

